P201 Menu
Class_Notes
Newton's Laws
1. Law of Inertia A body naturally moves in a straight line
at constant speed natural means no external influence on body
or:
Sum Forces ON body = 0
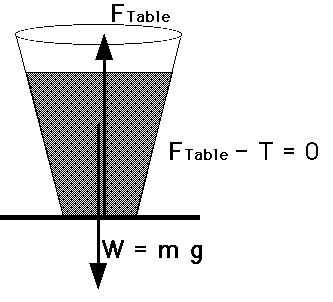
2. Law of Non-Inertia. The net force ON a body causes an acceleration
in direction of net force and of magnitude given by
Sum of Forces ON body equals mass x acceleration.
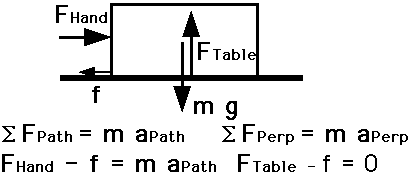
3. Law of Action - Reaction. ALL Forces are interactions
between two bodies (A & B) If body A exerts force on body
B (FAB), then body B exerts a force on body A (FBA) which
is equal and opposite. FBA = - FAB
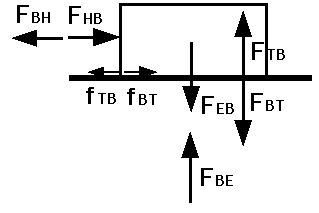
Other examples:
Conical Pendulum
Newton's Law for rotation
Whirlygig
Toronado Bottle
Now on to Horse and Wagon
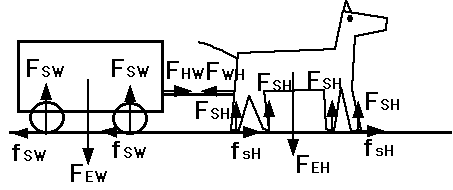 Apply 2nd Law to Wagon (4 wheels)
Path: FHW - 4 fSW = Mw apath
Perp: 4 FSW - FEW = Mw aperp
Apply 2nd Law to Horse (4 feet)
Path: 4 fSH - FWH = Mh apath
Perp: 4 FSH - FEH = Mh aperp
Apply 2nd Law to Wagon (4 wheels)
Path: FHW - 4 fSW = Mw apath
Perp: 4 FSW - FEW = Mw aperp
Apply 2nd Law to Horse (4 feet)
Path: 4 fSH - FWH = Mh apath
Perp: 4 FSH - FEH = Mh aperp
Other applications
Car Moving to Right
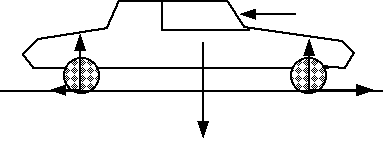
Car Coming At You and curving to right (your left)
Level Road ..................Banked Road
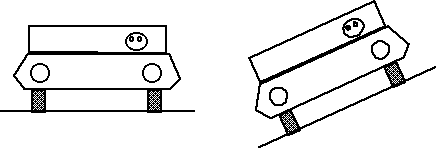 Now a little quiz about Newton's Laws
Now a little quiz about Newton's Laws
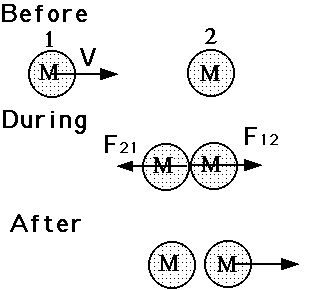
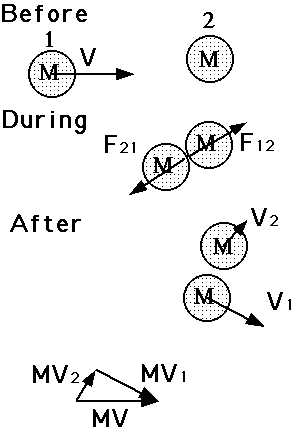
Concept of Collisions.......Explosions.
Application of Newton's 2nd and 3rd Laws.
F = m a or F = D(mv)/Dt
Or F Dt = D(mv)
Where D = delta (change)
mv = momentum
so force equals the rate of change of momentum of a body OR
Force acting for a time (Dt) causes a change in momentum.
For example, billiards
A: Head On Collision
B. Glancing Blow
Other examples:
Shooting guns
Shooting rockets
Interactive Physics
Apply 2nd Law to Wagon (4 wheels) Path: FHW - 4 fSW = Mw apath Perp: 4 FSW - FEW = Mw aperp Apply 2nd Law to Horse (4 feet) Path: 4 fSH - FWH = Mh apath Perp: 4 FSH - FEH = Mh aperp
Now a little quiz about Newton's Laws