Forest Ecosystems In A Changing World
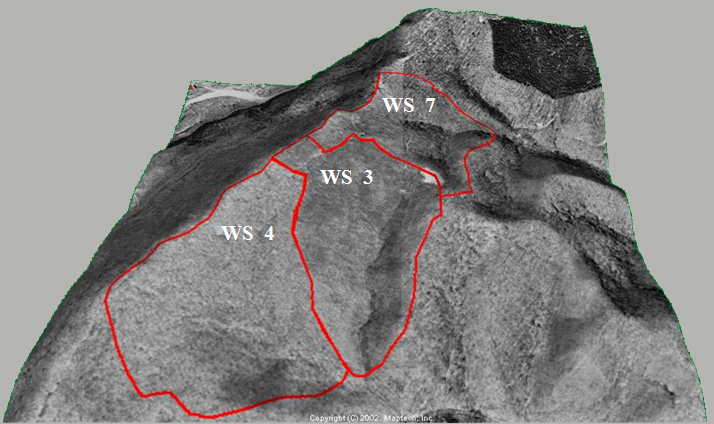
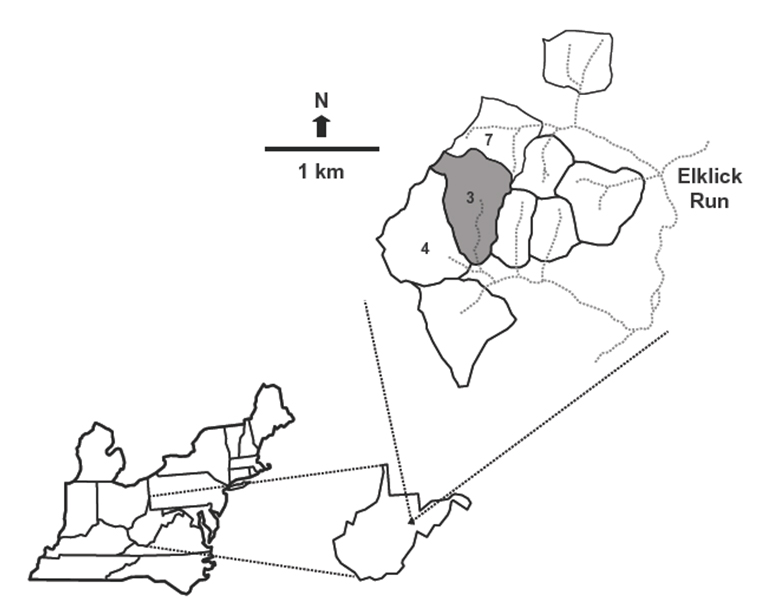
Aerial image of watersheds used in the acidification experiment.
Aerial application of ammonium sulfate to WS 3 began in 1989 and was initially done by helicopter.
Change in base flow stream pH following the start of fertilizer application (dashed line) to WS 3.
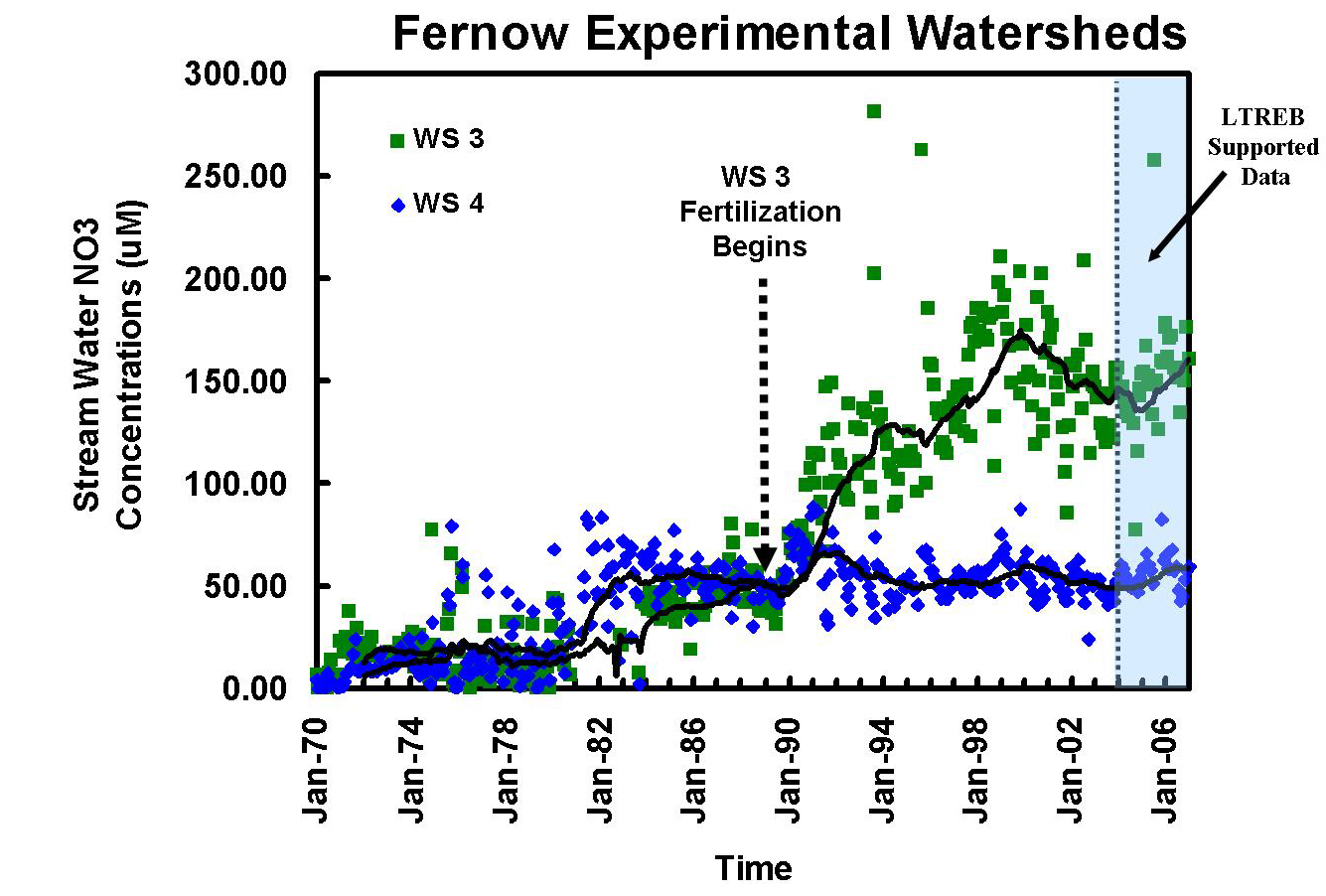
Long-term stream-water nitrate concentration for WS 3 and the adjacent reference watershed (WS 4).
 Whole-Watershed Acidification Experiment
Whole-Watershed Acidification Experiment
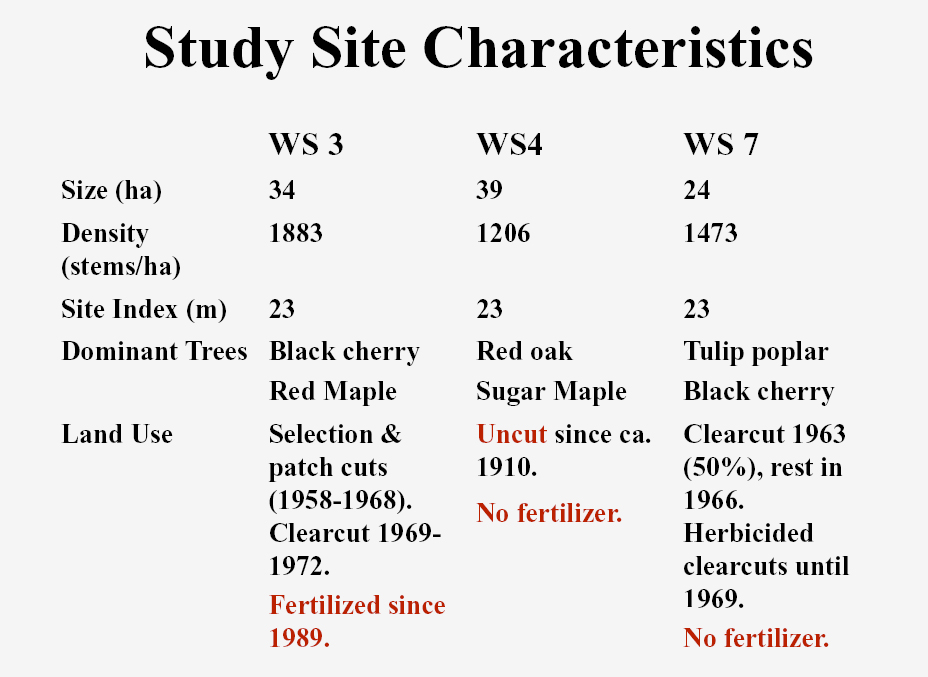
This experiment is being conducted on watershed 3 (WS 3), which is adjacent to reference WS 4 at the Fernow Experimental Forest. Watershed 3 is 34.3 ha in size with an average slope of 27% and a southerly aspect. Measurements of streamflow began in 1951 and measurements of stream-water chemistry began in 1970. Trees greater than 12.7 cm in diameter at breast height (dbh) were cut in 1958-1959, and again in 1963. Between July 1969 and May 1970, WS 3 was clear cut to 2.5 cm dbh except for a 2.99-ha riparian buffer strip. The buffer strip was clear cut in November of 1972. After each cut, the vegetation regenerated naturally. The dominant tree species growing on this watershed are black cherry, red maple, sweet birch, and American beech. Aerial applications of fertilizer on WS 3 began in 1989 when the trees were ~ 19 years old. Since then, granular ammonium sulfate has been applied three times each year: 7.1 kg N/ha and 8.0 kg S/ha in March and November, and 21.3 kg N/ha and 24.5 kg S/ha in July. The total amounts of N and S added each year (35.5 kg N/ha & 40.5 kg S/ha) are approximately twice the ambient amounts of N and S received as throughfall in adjacent WS 4 (Helvey and Kunkle 1986).
To assess treatment effects, measurements on WS 3 are compared to values measured on a nearby watershed with a forest of similar age – watershed 7 (WS 7). Watershed 7 is 24.2 ha in size with an easterly aspect. Measurements of streamflow began in 1956 and measurements of stream-water chemistry began in 1970. The upper half of WS 7 was clearcut in 1963 and then maintained barren with herbicides. The lower half was clearcut in 1966 and then maintained barren with herbicides. Herbicide applications on both halves were stopped in 1969 allowing the vegetation to regenerate. Currently the vegetation on WS 7 is dominated by black cherry and yellow poplar.